 |
 |
| Neurofunction > Volume 18(1); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN), a long-term disorder affecting the trigeminal nerve, is a form of debilitating neuropathic pain. Although the underlying pathogenesis of TN is debatable, loss of myelin along the trigeminal nerve due to direct compression from a blood vessel or secondary to other conditions such as multiple sclerosis or stroke is thought to be the principal cause. Paroxysmal sporadic pain, with unilateral onset, is the main phenomenon of TN. TN is typically diagnosed clinically. Medications, surgery, and complementary techniques are among the current therapy options for altering the neural circuits associated with TN. Nevertheless, anti-epileptic and tricyclic antidepressant medications are recognized as first-line treatments, and surgical treatment may be required for patients who have not obtained a therapeutic effect with at least three medications, have experienced intolerable side effects, or have symptoms that are not resolving. Stimulation of brain regions is an emerging off-label technique that has the potential to offer pain relief from TN, but sufficient data and more extensive studies on both animals and humans are yet to be published. More specifically, convenient diagnostic techniques and affordable treatment modalities for TN have become crucial needs in order to reduce the psychological and socio-economical losses caused by TN.
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN), also known as “tic douloureux,” is a recurrent, unilateral, brief (seconds to minute) facial pain syndrome characterized by paroxysmal electric shock-like or stabbing pain attacks that are sharp in initiation and termination and confined to the trigeminal nerve’s distribution [1]. With a yearly incidence of 4-29 per 100,000 people, TN is projected to have a lifetime prevalence of 0.16% to 0.3%. Females appear to be slightly more susceptible to TN than males (female:male ratio, 3:2). TN is uncommon in those under the age of 40, with an average onset age of 53-57 years [2].
The trigeminal nerve root is compressed by vessels in the posterior fossa in 80% to 90% of cases of the TN. The superior cerebellar artery, anterior inferior cerebellar artery, vertebral artery, and petrosal vein are blood vessels linked to trigeminal nerve compression. Continuous or recurrent nociceptive inputs from the head and neck congregate on the spinal trigeminal nucleus, within which neurotransmitter and vasoactive substance discharge is enhanced, lowering the threshold of adjacent second-order neurons that receive input from sites apart from nociceptive sources, as per the trigeminal convergence-projection theory. The thalamus (i.e., the ventral posteromedial), limbic system, and somatosensory cortex receive the signals from these stimulated second-order neurons, which are subsequently interpreted as pain (Fig. 1) [3]. Multiple sclerosis (MS), arteriovenous malformation or saccular aneurysm, epidermoid cyst, acoustic neuroma and meningioma are some of the other reasons that can cause secondary TN. They originate as a result of MS or other illnesses demyelinating the trigeminal nerve nucleus whereas idiopathic TN is not linked with any neurological or other lesion that may be diagnosed by clinical assessment [4].
TN is a type of persistent, episodic, and recurrent neuralgic pain that can be distracting at best and completely incapacitating at worst. Depending on the existence or lack of an evident disease process that could characterize the neuralgia, the International Classification of Headache Disorders (3rd edition) defines TN into three groups: classical TN, secondary TN, and idiopathic TN [5]. Because clinical indications differ from patient to patient depending on which dermatome/s are afflicted, the exact intensity of pain, and the presence or absence of background pain, TN diagnosis can be difficult. Many documented cases are idiopathic, implying they have no obvious cause. Although intracranial lesions that compress or irritate the trigeminal nerve are rare, they are a detailed cause of secondary TN. They are generated by MS, as well as space-occupying lesions such cerebellopontine angle tumors and meningiomas. Classical TN is characterized by paroxysmal and electric shock-like pain and is caused primarily by demyelination due to blood vessel tension on the trigeminal root entrance zone [6]. These exhibit evident nerve compression findings in the trigeminal nerve with morphological alterations, and causal issues can be seen with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and surgery. Idiopathic, on the other contrary, is not linked to MRI or electrophysiological aberrations. There are a range of factors for TN, and clinical facts on every variety could encompass the entire the underlying mechanisms [7].
The foramen rotundum, foramen ovale, and foramen spinosum are smaller on the right side than on the left, resulting in a higher incidence of TN on the right side. There were no occurrences of TN pain only involving discomfort in the V1 division’s innervated region. Although V2 and V3 pain coexisted in almost a fifth of patients, V1 and V2 pain only coexisted in 2.4%. If pain impacts numerous branches of the trigeminal nerve, the prospect of referred pain should be addressed. When it pertains to pain distribution laterality, the right V2 has become the most common site [7].
TN is more common in female patients, and is more common in elderly people. Due to the sheer unexpected quick stabbing and strong character of the paroxysms, patients commonly recall the onset of TN as memorable. In 87% of cases, stabbing paroxysmal pain was the first symptom. Other 13% showed the emergence of a rather subtle and prolonged pain before the typical paroxysmal pain, which is also referred as “pretrigeminal neuralgia” and evident by periods of aggravation and diminution. It is usual to have a latent phase of several minutes during which a paroxysm cannot be induced. Certain individuals with long-term TN may experience a dull ache that persists between pain paroxysms. TN, unlike the other facial pain disorders, does not usually keep patients awake at night [8].
The maxillary (40%) and mandibular (39%) branches of the trigeminal nerve were revealed to be among the most frequently afflicted in an investigation on the clinical status of TN. Only paroxysmal pain lasted shorter than 1 minute for three thirds of the total patients. Approximately 90% of patients experienced pain-free bouts at least once. Chewing (88%), brushing teeth (82%), washing face (79%), and talking (70%) were the most prevalent triggering variables. These kinds of triggers, on the other hand, are basically neutral stimuli in normal people. Individuals often tend to point to the trigger zone with one finger and specify the actions that start off an attack. Most people with TN have both spontaneous and stimulus-evoked pain. There may be only a few attacks a day in mild cases, but there may be repetitive rail of strikes that last minutes to hours in extreme situations. Dread of launching attacks may render the affected person inert. The episodes may last for days, weeks, or months before subsiding, reducing in frequency or ceasing entirely. They constantly show up, with exacerbations becoming more prevalent as people age [9].
The three main indications are used to establish a clinical diagnosis of TN: pain limited to the territory of one or more divisions of the trigeminal nerve; paroxysmal pain described as a “shock” or “electric sensation”; and pain caused by harmless stimuli on the face or intraoral trigeminal territory. TN is associated with triggered paroxysmal pain, which is reported by 91% to 99% of patients, suggesting that this trait may be pathognomonic for the condition [8].
In TN, structural abnormalities are linked to pathologic demyelination and remyelination of the wounded nerve, which is a common feature in both humans and animal models of chronic nerve compression. With trigeminal nerve compression, there is evidence of axonal degeneration and Schwann cell injury. Schwann cells undergo significant apoptosis and persistent downregulation of myelin-associated glycoprotein resulting from chronic nerve compression injury, and given Schwann cells’ ability to inhibit axonal growth via myelin-associated glycoprotein expression, loss of this intrinsic growth regulation could result in the axonal sprouting seen in classic TN [10].
Although neurovascular compression is the most common cause of TN, it can also be caused by primary demyelination disorders. Patients with MS are twenty times more likely than the general population to experience neuropathic pain. Lesions in second-order sensory neurons in the brainstem ipsilateral to the afflicted side were found in a group of individuals with comorbid TN and MS, which are hypothesized to be responsible for trigeminal pain and other orofacial sensory problems. Patients affected with MS or a brainstem infarction have been linked to intrapontine demyelination along the trigeminal afferent and trigeminal nucleus, which are associated with TN symptoms. Concurrent neurovascular compression on the trigeminal nerve may hasten demyelination in MS patients, resulting in TN [11].
Researchers can now evaluate the sensitization of central nociceptive and emotional processing in patients with classical or idiopathic TN using modern electrophysiological and functional imaging techniques.
In TN patients, nociceptive signal transmission is amplified. Electrophysiological recordings exhibited that pain-related evoked potentials are markedly enhanced in all trigeminal divisions on both symptomatic and non-symptomatic sides in TN patients with associated chronic facial pain. The channelopathies and pathologic changes in the architectures of afferent neurons cause the trigeminal nerve to become functionally hyperexcitable, as seen in TN. In fact, recordings of trigeminal nerve roots in traditional TN models revealed ectopic action potential production and extended after-discharges in demyelinated neurons [12].
TN is functionally connected to voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channel dysregulation. Nav1.3 was found to be significantly upregulated in both preclinical and clinical cases of TN, whereas, downregulation of Nav1.7 has also been reported. Upregulation of additional Nav channels, such as Nav1.1, has also been associated to excitation of the trigeminal nerve in a chronic constricted nerve injury model in rodents [13]. In addition, in preclinical models of classical TN, hyperexcitability in trigeminal neurons has been discovered as a result of dysregulation of the resting potential mediated by the voltage-gated potassium channel. Along with the voltage-gated channels, painful attacks in TN patients increase activity in areas that are traditionally associated with pain-related sensory processing (trigeminal nuclei, thalamus, and somatosensory cortices) [14].
Since the three types of TN (classical, secondary, and idiopathic) might be clinically identical, MRI with gadolinium is recommended to rule out MS and cerebellopontine masses during the diagnosis. The fast advancement of MRI technology has aided in the identification of some of the more noticeable anatomical changes in TN. New MRI investigations, such as voxel-based morphometry, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), three-dimensional time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery DTI-sequences have provided new insights into the etiology of TN. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that changes in brain activity related with stimulation of the cutaneous trigger zone in individuals with TN may be studied using functional MRI [15].
The use of MRI and three-dimensional reconstruction can reveal neurovascular compression. The neuroimaging techniques include three-dimensional T2-weighted MRI sequences with extensive investigation of the cisternal and cavernous parts of the nerve, TOF MRA for artery visualization, and phase-contrast MRI for vein visualization. Several studies have suggested that using DTI and tractography to reveal focal demyelination and edema, microstructural alterations in the nerve at locations of vascular compression can be assessed. Neurovascular compression at the trigeminal nerve root entrance zone corresponds highly with TN symptoms and morphological nerve alterations, such as nerve atrophy, displacement, indentation, or flattening, according to high-resolution pictures [16-18].
Furthermore, structural and functional neuroimaging analysis showed considerable changes in functional connectivity of the frontal-limbic circuit, as well as gray matter loss in pain-modulating, sensory-motor, and emotional circuits, when TN patients were compared to healthy people. Using voxel-based morphometry, researchers discovered a gray matter volume loss in TN patients in the primary somatosensory and orbitofrontal cortices, as well as the thalamus, insula, cerebellum, and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Similarly, DTI revealed a decreased fractional anisotropy in TN patients’ trigeminal nerves and white matter in the brain, indicating that structural abnormalities in the trigeminal nerves exist in TN, even if they are not visible on gross imaging [19,20].
The array of differential diagnoses is vast and varies based on the context. Cluster headaches or migraines, post-herpetic neuralgia, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder are indeed conditions that are likely to be confused with TN. It’s plausible that TN is mistaken for tooth discomfort. Dental pain is frequently constant, bland or agonizing intraoral pain, whilst classic TN is invariably transient and intense pain. From a diagnostic and treatment standpoint, distinguishing between TN and trigeminal neuropathy caused by (dental) trauma is critical [21]. The unpleasant sensations with TMJ dysfunction may have traits that are identical to secondary neuralgia, which can make differential diagnosis challenging. When examining other disparities, the occurrence of the disorders must also be regarded. The autonomic symptoms that occur unilaterally with the intermittent pain include conjunctival injection or tears, miosis, ptosis, sweating, and stuffy nose. These can emerge in the V1 trigeminal area in conjunction with TN attacks. The incidence of TN has been linked to regular and daily tasks [8].
Anticonvulsant medicines are the cornerstone of TN treatment. Phenytoin was the first medicine used to treat TN, and it was shown to be effective. However, two medications are recommended as first-line therapy in TN, according to the most recent European Federation of Neurological Societies guidelines: carbamazepine (CBZ; 200-1,200 mg/d) and oxcarbazepine (OXC; 600-1,800 mg/d). Because of its better tolerability and lower risk of medication interactions, OXC is frequently utilized as a first-line treatment for TN. CBZ’s usefulness has also been established in a number of trials. Both CBZ and OXC are Nav blockers that attempt to calm agitated neuronal membranes and diminish aberrant nociceptive output in TN patients. Despite their effectiveness, the side effects of these drugs involve sleepiness, nausea, rashes, ataxia, increased liver enzymes and electrolyte imbalance, which limit their use [22,23].
If the first-line anticonvulsants are unsuccessful or poorly tolerated, alternative anticonvulsive medications such lamotrigine, gabapentin, pimozide, tocainide, and pregabalin can be used as second-line or monotherapy. Another Nav blocker, lamotrigine, has been shown to have an analgesic effect when used as a second drug in a limited number of patients with refractory TN. The evidence to use gabapentin, a voltage-gated calcium channel blocker (CCB), in TN was reviewed in a meta-analysis assessing gabapentin to CBZ [24,25].
Moreover, botulinum toxin A (BTX-A), a neurotoxin produced from the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, has been shown in many randomized controlled studies to be a successful maintenance treatment for TN. The BTX-A is considered to provide a better analgesic impact when injected directly into the trigger points. For up to 12 weeks, single session has been demonstrated to reduce anxiety, sadness, insomnia, fatigue, pain, and the frequency of attacks per day. But, patients frequently experience facial disproportion with maneuvering and puffiness subsequent BTX-A injections owing its neurotoxic and paralytic action [26].
Finally, based on traditional Chinese medicine beliefs, manual acupuncture and electroacupuncture may be useful adjuvant therapy for TN. The amplification of peripheral acupuncture sites is thought to elicit brain nociceptive modulation and upregulation of the endogenous opioid pathway. It’s worth noting, though, the significant clinical evidence to back up these procedures is currently absent [27].
In complement to maintenance therapy, several medications have been investigated to be used as a preventive cure amid acute attacks. In individuals with second-division TN, nebulized spray of 8% lidocaine showed correlative pain relief over 4 hours [28]. Another Nav blocker, intravenous phenytoin, showed an acute response rate of 89% in a retrospective subset of patients with all types of TN [29].
Although surgical techniques can help lessen the intensity and likelihood of TN strikes in the appropriate patients, they are usually reserved for when regular pharmaceutical doses are insufficient to control symptoms or when side effects limit continuing usage.
This surgical procedure, which is now rarely done, involves neurectomy, alcohol injections, or the creation of radiofrequency lesions or cryolesions at the emergence of trigeminal nerve branches from the facial bones. The goal of these operations is to create an anesthetic area on the face that matches to the injured nerve’s distribution. However, clinical trials have not fully substantiated the benefits of such treatments, and the strategies frequently resulted in numbness [24].
When a patient is unable to endure surgical procedures or does not have revealing vascular compression, percutaneous approaches like balloon compression, radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT) and chemical rhizotomy can be used to percutaneously hinder the trigeminal ganglion (TG) in Meckel’s cave or exiting branches.
RFT causes small-diameter pain fibers to be damaged more than large-diameter pain fibers. This technique is based on the trigeminal nerve and Gasserian ganglion rootlets being electrocoagulated. The electrode is meant to avoid injuring the first branch of the trigeminal nerve in order to avoid corneal deafferentation and keratitis. Initial pain alleviation was found to be greater than 90%, with a recurrence rate of up to 25%. Masticatory weakness, dysesthesia, and ocular numbness have all been recorded as side effects, and they seem to be linked to substantial individual variation in somatotopic arrangement of trigeminal nerve fibers and irreparable injury to C fibers [30].
Another approach for treating TN is percutaneous balloon compression (PBC), which involves abrasing afferent fibers at the level of the Gasserian ganglion. Because of its low cost, ease, and benefits of being the only percutaneous technique performed with the patient under general anesthesia, PBC has been broadly employed. It also has an excellent ratio of rapid postsurgical pain reduction, spanning from 80% to 90%, and a period of time devoid of discomfort that varies from 2 to 3 years without the use of medication. However, there are no findings on these patients’ long-term quality of life in the literature. Issues such as numbness, dysesthesia, and, in rare cases, masseter instability are common and usually resolve following a few months; cranial nerve deficits and meningitis are far less prevalent. Moreover, in terms of compression duration and compression pressure, there are no established requirements [31].
Chemical ablation of pain-transducing nerve fibers is used in percutaneous glycerol rhizotomy. Pain alleviation in individuals with TN caused by demyelination and axonal fragmentation is determined by injecting glycerol into the trigeminal cistern. This procedure has remained basically constant since its introduction, with a reported immediate pain alleviation rate of almost to 90% and a proportion of pain-free patients at 3 years of over 50%. Dysesthesias, herpes labialis, ocular numbness and masseter weakness have all been recorded as common side effects [32].
Microvascular decompression (MVD) is the first-line operative therapy for patients with a definite neurovascular compression cause as established by neuroimaging. Three-dimensional rapid imaging using a steady-state acquisition procedure has recently been introduced, resulting in a absurdly high-resolution T2-weighted MRI with outstanding contrast amongst structures, such as the CSF, trigeminal nerve, and nearby blood arteries, as well as TOF MRA. MVD has a well-established track record of success, with a pain-free rate of roughly 70% after the first 2 years postsurgery. It has turn out to be foremost therapies for TN because it provides long-term pain alleviation. Even so, not every patients who undergo MVD have a positive prognosis. The average pain-free period post MVD spans from 0.6 to 10 years without drugs. After 5 years, the proportion of subjects that are pain-free varies from 58% to 78% [15,33].
The average surgery-related death rate is 0.3%. Cerebrospinal fluid leaks affect 2.0% of patients, brain stem infarctions or hematomas affect 0.6% of patients, and meningitis affects 0.4% of patients. In few patients, sensory loss in part or most of the trigeminal nerve sensory distribution on the face occurs. Ipsilateral hearing loss is the most concerning long-term consequence, notwithstanding its rarity (incidence of 1.8%). Although individuals with MS who have drug-resistant TN may be provided MVD, there is inadequate evidence to justify or contradict the efficacy of surgical intervention of TN in MS patients [24,34].
In few centers, Gamma-knife radiosurgery has been utilized to treat patients coexisting health issues who may not have been potentially suitable for MVD or who refused further invasive procedure. Typically, the trigeminal nerve’s root entry-zone is chosen as a point, with dose regimes ranging from 70 to 100 Gy. The precise determination of the trigeminal root coordinates prior to their entry into the pons, where the radiation beams must be collimated to prevent injuring the pons, is a problem of this process. The pain-relieving impact of gamma-knife stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) takes 6 to 8 weeks to develop, in contrast to the instantaneous pain reduction associated with percutaneously produced TG lesions. One to 2 years after the treatment, 24% to 71% of patients report continuing pain alleviation, and 4 to 5 years later, 33% to 56% report continued pain relief. In spite of that, because the underlying mechanisms are not completely known, there is still some doubt about the precise target and ideal dose to utilize. The root access zone of the trigeminal nerve, located 2-3 mm from the brainstem surface, is employed in several clinical target volume definitions. The brainstem trigeminal nuclei or the thalamic centromedian nucleus are other potential targets. Elevated doses of radiation are associated with better consequences in general, but problems raise at doses larger than 90 Gy [24,35].
Since its introduction by Leksell, non-invasive SRS has been reported to be a promising therapeutic option for TN. The use of a linear accelerator and robotic-assisted SRS for TN treatment has become more common in recent years. Although it is not a curative for TN, it is a viable treatment choice due to its acceptable effectiveness even in pretreated and MS-related patients [36].
Motor cortex stimulation (MCS) and deep brain stimulation (DBS) have both been stated as alternative therapies for persistent pain that has resisted standard medical and surgical treatment. Several studies have shown employing MCS to treat TN produces excellent results, typically 75% to 100% of patients experiencing consistently good pain reduction. Nonetheless, these researches are mostly focused on the application of MCS in the treatment of pain syndrome. On the other hand, in a comprehensive study, authors found that yet none of the four patients with refractory TN responded to the procedure, but all five patients having refractory TN related to MS who had DBS saw a substantial reduction in pain episodes inside the first trigeminal branch [1,37].
Although TN has explored a broad range of drugs, the scientific literature has underlined the necessity for high-quality clinical trials. LibraTN, an investigational novel drug from Noema Pharma that acts on the mGluR5 inhibitor NOE-101 in TN, is recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration to commence a phase 2b clinical investigation. In a preceding phase 1 study, it was proven safe and well tolerated in adults (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT05217628). The safety and efficacy of guanfacine pairing with lidocaine for trigeminal nerve block techniques for treating pain in TN patients are also being examined in another clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03865940). The steady hunt for advanced drugs has preceded to development of several new medicines that lessen the electrical activity of an otherwise excited nerve by intervening across novel pathways. Vixotrigine is a potent sodium channel blocker which prevents seizures or unpleasant stimuli by particularly prioritizing higher frequencies. A cross‐sectional prospective phase III trial is actively being undertaken, and the outcomes may provide additional insight on this drug. Eslicarbazepine belongs to the dibenzepine class of third-generation antiepileptic drugs. The drug is now licensed as an additional therapy for focal seizures since it targets voltage-gated sodium channels. For treating pain in TN, emerging drugs for instance eslicarbazepine and vixotrigine are being assessed [38].
Sumatriptan is a 5-hydroxytyptamine receptor (1A/B/C) agonist as well as a blocker of the 5-hydroxytyptamine receptor (1A/B/C). Migraine and cluster headaches have been effectively treated with it. At the damaged trigeminal nerve root, the drug limits vasodilation and demyelination. Two-randomized controlled trials explored the effect of sumatriptan 3 mg subcutaneous injections and oral delivery of 50 mg twice daily. In hyperactive neurons, intranasal CO2 has long been thought to be a pain modulator. This is relied on the theory that CO2 promotes a drop in mucosal pH, thereby triggers the nociceptive impact of primary trigeminal afferent neurons [39].
In patients who have not been eased by sodium channel blockers alone, CCBs and antidepressants have been recommended. Misoprostol is a prostaglandin E1 analogue that has been shown to alleviate pain in TN patients with associated MS in case studies. Capsaicin, topical or intranasal lignocaine are among the several treatment options available, although their extensive use is not advised at this point [38].
Today, research has contributed to a greater comprehension of the causes and pathways of pain, and progress continues to associate with improved TN diagnosis and treatment. Preclinical and clinical studies have contributed significantly to our understanding of all aspects of TN, but further research is certainly needed to fill in the disparities and promote to the development of existing therapies and the quest for novel therapeutic possibilities. Here, we attempt to include the recent TN research in rodents and human subjects.
A study proposed that emodin (active anthraquinone constituent of rhubarb extract) may diminish ERK1/2 phosphorylation and p38 in TG through decreasing P2X3 receptor activation and inhibiting calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) production. Inhibition of P2X3 receptors in TG nociceptive neurons caused by increased glutamate transmission could be a new focus for orofacial neuropathic pain therapy. Pannexin 1 may activate metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) expressed in TG nociceptive neurons that innervate the orofacial area, allowing glutamate discharge from both TG and satellite glial cell. It’s possible that mGluR5 signaling increases P2X3 receptor expression in TG nociceptive neurons, resulting in orofacial mechanical allodynia. Upregulation of the P2X3 receptor increased CGRP synthesis in TG neurons, adding to pain and allodynia, and CGRP expressed by peripheral sensory neurons is linked to neuropathic pain pathogenesis [54]. Metabolomics assays has been used to study the metabolic patterns underpinning depression caused by TN in a cobra venom intra-ION induced TN rodent model. Curcumin therapy in rats with TN may reduce mechanical allodynia and depressing actions through modulating metabolites and metabolic pathways [55].
According to Zhang et al. [56], persistent TN causes despair, which is produced by intensified dopamine neuron activity in the midbrain. The enhanced activity of dopamine neurons is due to neural pathways connecting the spinal trigeminal subnucleus caudalis, the ventral tegmental region and the lateral parabrachial nucleus. In a rodent study, it was found that TN can cause neurodegeneration by upregulating the expression of CD95/CD95L, resulting in increased neuroinflammation and neuronal death [57].
In the infraorbital nerve-chronic constriction injury (ION-CCI) paradigm, another study found that peripherally employed botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT-A) can yield antinociceptive results. BoNT-A may operate directly on the Vc by way of axonal transport, inhibiting excessive TRPA1, TRPV1 and TRPV2 expression, and reducing central sensitization as the underlying processes [58]. Modulation of the VLO-periaqueductal gray matter projection had no influence on TN-induced anxiodepressive responses that suggests a possible innovative mechanism-based therapy method for neuropathic pain’s anxiodepressive effects.
Trigeminal nerve damage causes demyelination, which is thought to be a major cause of TN. Meantime, trigeminal semilunar ganglion’s neurons are engaged to produce the ignition focus. These neurons are stimulated and emit aberrant signals when the trigeminal nerve peripheral branches are compressed or stimulated by inflammation. Schwann cells have also been implicated in TN and have been proven to have a pain-relieving impact by remyelinating damaged nerves in some investigations [59].
Mechanical compression lesion in the TN animal model’s trigeminal nerve generated glial plasticity in the trigeminal root entrance zone, which constantly modified the glial functionality of the central nervous system-peripheral nervous system transitional area, as per a study. The activation of adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK) in the glia of the spinal trigeminal nucleus (secondary TN) by resveratrol is useful in the treatment of CCI-induced neuroinflammation, and it also suggests that AMPK could be a new focus for the TN treatment. The Ca2+ activated K+ (SK3) channel, which has a small conductance, may take part in a key role in the TN etiology and could be a possible target for treatment [60].
In the early stages, stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous (SHED) teeth transplanted at the injury site condensed inflammatory cell infiltration and proinflammatory cytokines in the injured nerve, as well as inhibiting CCI-ION-induced TRPV1 expression upregulation in the trigeminal nerve and ganglion. These findings support the application of SHED in the TN treatment in a preclinical setting [61].
Human neuroimaging studies demonstrate structural and functional abnormalities in the different brain regions in TN pain, in addition to the rodent research. A study found that volume recovery or normalization reveals sex-specific hippocampus plasticity in TN, with females experiencing a higher volumetric increase than males. They hypothesized that hippocampus shrinkage in TN is caused by pain, and that proper treatment can correct these anomalies [62].
In patients with typical TN, altered anatomical and functional connectivity between the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex may underpin the aberrant salience network and present an alternate target for treatment therapies. Using ultra-high field MRI, an initial analysis of structural abnormalities in the trigeminal nerve and subnuclei of limbic regions in TN patients. This support the hypothesis that TN pathophysiology is a complicated mix of local structural changes in the trigeminal nerve, along with changes in the structure and function of numerous brain areas involved in nociception and pain processing directly and indirectly [63].
The role of RFT in pain therapy for TN patients was investigated in the systematic study. RFT provided a high rate of early pain alleviation and a long period of pain-free time after treatment. In longitudinal, perioperative neuroimaging study, because atrophy of the contralateral thalamus is a common feature in patients with medically refractory TN, local alteration in preoperative thalamic structure and very early postoperative metabolic changes in the thalamus both play a role in influencing the durability of pain relief after TN surgery [64].
Further prospective and longitudinal clinical investigations, as well as basic translational TN research, might aid to adapt the discrepancy in the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying TN and pave the way for innovative therapies in the future.
TN is a devastating condition that is difficult to detect and treat for both neurologists and neurosurgeons. The main cause of difficulty could be a lack of understanding of the complicated etiology, pathogenesis, and pathophysiology. However, in recent years, promising advances in the treatment of TN have been made with the discovery of novel medications and the implementation of innovative surgical procedures. Therefore, more research into the core causes of TN, as well as innovative therapeutic methods, could enhance the accuracy of diagnosis and treatment for patients suffering from this devastating condition.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF, 2020R1F1A1052716), the Brain Korea 21 FOUR of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 5199990614277). This study was additionally supported by the “Regional Innovation Strategy (RIS 2021RIS-001 and 2021RIS0438)” through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE).
Fig. 1.
Trigeminal neuralgia pathway. SP: substance-P, CGRP: calcitonin gene-related peptide, VPM: ventral posteromedial.
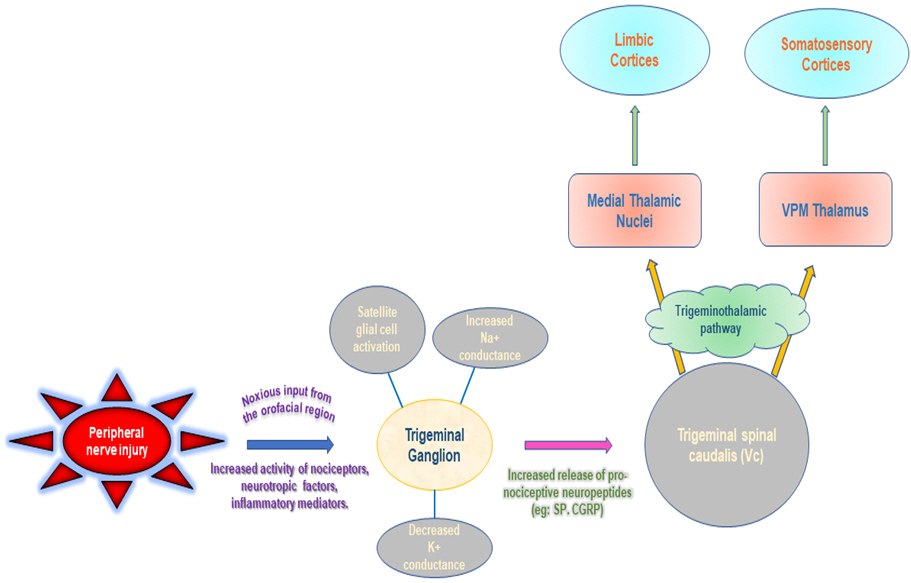
Table 1.
Experimental animal models for research on TN
| TN animal model | Brief model preparation technique | Reference (year) |
|---|---|---|
| Unilateral chronic constriction injury of the distal ION in rats | Starting at the posterior end of third row of whisker lines, a small incision parallel to the midline was made toward the ipsilateral orbit. The superficial fascia was abruptly removed to reveal the ION trunk outside the ocular cavity at its distal section. Two chromic catgut ligatures were wrapped loosely around the ION’s distal end. | Ding et al. (2017) [40] |
| Trigeminal ganglion compression with 4% agar solution in rats | A 4% agar mixture was pumped into the trigeminal ganglion by a stainless-steel injector (24 gauge), which was prolonged 2 mm beyond the end of a guide cannula to compress the ganglion. | Ahn et al. (2009) [41] |
| Trigeminal root compression with polymer crystals in rats | Polymer crystals were administered in the space between the trigeminal sensory root and the temporal bone by stereotaxic polymer injection. | Yeomans and Klukinov (2012) [42] |
| Trigeminal nerve root compression in rats | From the inferior orbital fissure, a tiny plastic filament was retrogressively introduced into the intracalvarium until it contacted the trigeminal nerve root for compression. | Luo et al. (2012) [43] |
| Cobra venom to the ION in rats | A cut was made to reveal the fossa orbitals and nasal bone. The ION was dissected freely at its rostral limit in the orbital region, gently lifted, and cobra venom (0.4 mg lyophilized entire venom/4 L saline) was infused into the ION’s nerve sheath. | An et al. (2011) [44] |
| Chronic constriction injury of the ION in rats or mice | After making an incision above the left eye along the arc of the frontal bone, the ION was gently separated from the adjacent fascia, muscle, and connective tissue. The ION was then mildly constricted with two ligatures set 3-4 mm apart and fastened till it was slightly confined. | Islam et al. (2021) [3] |
| CFA or formalin-induced pain in mice | 5 µL of CFA was injected subdermally into the rostral external part of the ear, or 10 µL of 4% of formalin was injected subcutaneously into the whisker pad. | Tzabazis et al. (2014) [45] |
| FRICT-ION in mice | In the narrow area where the ION enters through the rigid infraorbital foramen, 3 mm of chromic gut suture was introduced intraorally. | Montera and Westlund (2020) [46] |
| Peripheral ION ligation in mice | In a recumbent position, the oral cavity was exposed to detect the left tendon of the masseter muscle on the top portion of the oral cavity. A 1-mm incision was made in front of the tendon to expose the ION, and one end of the ION was ligated using 6-0 silk suture. | Zhao et al. (2021) [47] |
| Partial transection of the ION | Using angled clamps, a cavity in the left palate was exposed, and the ION under the mucosa was accessible. The ION’s deep branch, which innervates the ventral edge of the left vibrissal pad and upper lip, was strongly tied with catgut, and the distal end was cut open to remove a 1-2 mm section. | Li et al. (2020) [48] |
| GabrgI knock-in mice | Model generation was done by using CRISPR/Cas9 by a TN-associated de novo mutation (p.Cys188Trp) in the GABAA receptor Cl channel-1 subunit (GABRG1). | Dong et al. (2020) [49] |
| Incorrectly positioned dental implants in rats | To damage the inferior alveolar nerve, the left lower second molar was substituted with a small dental implant. | Li et al. (2019) [50] |
| TRESK knock-out mice | TRESK knockout mice were produced by traversing heterozygous breeders (Kcnk18tm1(komp)Vlcg). | Guo et al. (2019) [51] |
| Transgenic mice that overexpress TNF-α | TNFglo mice were bred with Nav1.8-Cre mice to make TNF-α cTg mice that overexpressed TNF-α specifically in nociceptive neurons. | Rozas et al. (2016) [52] |
| Talcum powder administration to the peripheral ION in rats | Talcum powder (30%, 0.3 mL) was injected into the peripheral infraorbital foramen of animals. | Wang et al. (2018) [53] |
REFERENCES
1. Islam J, Kc E, Oh BH, Kim S, Hyun SH, Park YS. Optogenetic stimulation of the motor cortex alleviates neuropathic pain in rats of infraorbital nerve injury with/without CGRP knock-down. J Headache Pain 2020;21:106



2. Lambru G, Zakrzewska J, Matharu M. Trigeminal neuralgia: a practical guide. Pract Neurol 2021;21:392-402



3. Islam J, Kc E, Kim S, Kim HK, Park YS. Stimulating GABAergic neurons in the nucleus accumbens core alters the trigeminal neuropathic pain responses in a rat model of infraorbital nerve injury. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:8421



4. Godazandeh K, Martinez Sosa S, Wu J, Zakrzewska JM. Trigeminal neuralgia: comparison of characteristics and impact in patients with or without multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 2019;34:41-6


6. Bithal PK. Radiofrequency thermocoagulation for trigeminal neuralgia. In: Rath GP (ed). Handbook of Trigeminal Neuralgia. Singapore : Springer Singapore, 2019, pp141-50
7. Noguchi T, Shimamoto Y, Fukuda KI. Clinical characteristics of trigeminal neuralgia in a dental hospital. J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2021;21:431-40




8. Maarbjerg S, Gozalov A, Olesen J, Bendtsen L. Trigeminal neuralgia: a prospective systematic study of clinical characteristics in 158 patients. Headache 2014;54:1574-82


9. Gerwin R. Chronic facial pain: trigeminal neuralgia, persistent idiopathic facial pain, and myofascial pain syndrome: an evidence-based narrative review and etiological hypothesis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020;17:7012



10. Maarbjerg S, Di Stefano G, Bendtsen L, Cruccu G. Trigeminal neuralgia: diagnosis and treatment. Cephalalgia 2017;37:648-57



11. Laakso SM, Hekali O, Kurdo G, Martola J, Sairanen T, Atula S. Trigeminal neuralgia in multiple sclerosis: prevalence and association with demyelination. Acta Neurol Scand 2020;142:139-44



12. Obermann M, Yoon MS, Ese D, Maschke M, Kaube H, Diener HC, et al. Impaired trigeminal nociceptive processing in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Neurology 2007;69:835-41


13. Xu W, Zhang J, Wang Y, Wang L, Wang X. Changes in the expression of voltage-gated sodium channels Nav1.3, Nav1.7, Nav1.8, and Nav1.9 in rat trigeminal ganglia following chronic constriction injury. Neuroreport 2016;27:929-34


14. Abd-Elsayed AA, Ikeda R, Jia Z, Ling J, Zuo X, Li M, et al. KCNQ channels in nociceptive cold-sensing trigeminal ganglion neurons as therapeutic targets for treating orofacial cold hyperalgesia. Mol Pain 2015;11:45




16. Leal PR, Hermier M, Souza MA, Cristino-Filho G, Froment JC, Sindou M. Visualization of vascular compression of the trigeminal nerve with high-resolution 3T MRI: a prospective study comparing preoperative imaging analysis to surgical findings in 40 consecutive patients who underwent microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 2011;69:15-25. discussion 26



17. Shimizu M, Imai H, Kagoshima K, Umezawa E, Shimizu T, Yoshimoto Y. Detection of compression vessels in trigeminal neuralgia by surface-rendering three-dimensional reconstruction of 1.5- and 3.0-T magnetic resonance imaging. World Neurosurg 2013;80:378-85


18. Hughes MA, Frederickson AM, Branstetter BF, Zhu X, Sekula RF Jr. MRI of the trigeminal nerve in patients with trigeminal neuralgia secondary to vascular compression. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2016;206:595-600


19. Zhang C, Hu H, Das SK, Yang MJ, Li B, Li Y, et al. Structural and functional brain abnormalities in trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review. J Oral Facial Pain Headache 2020;34:222-35


20. Tang Y, Wang M, Zheng T, Yuan F, Yang H, Han F, et al. Grey matter volume alterations in trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2020;98:109821


21. Melek LN, Smith JG, Karamat A, Renton T. Comparison of the neuropathic pain symptoms and psychosocial impacts of trigeminal neuralgia and painful posttraumatic trigeminal neuropathy. J Oral Facial Pain Headache 2019;33:77-88


22. Kutluay E, McCague K, D’Souza J, Beydoun A. Safety and tolerability of oxcarbazepine in elderly patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 2003;4:175-80


23. Wiffen PJ, Derry S, Moore RA, Kalso EA. Carbamazepine for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;2014:CD005451



24. Bendtsen L, Zakrzewska JM, Abbott J, Braschinsky M, Di Stefano G, Donnet A, et al. European Academy of Neurology guideline on trigeminal neuralgia. Eur J Neurol 2019;26:831-49



25. Yuan M, Zhou HY, Xiao ZL, Wang W, Li XL, Chen SJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of gabapentin vs. carbamazepine in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a meta-analysis. Pain Pract 2016;16:1083-91


26. Zhang H, Lian Y, Ma Y, Chen Y, He C, Xie N, et al. Two doses of botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: observation of therapeutic effect from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Headache Pain 2014;15:65




27. Sun J, Li R, Li X, Chen L, Liang Y, Zhang Q, et al. Electroacupuncture therapy for change of pain in classical trigeminal neuralgia. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e19710



28. Kanai A, Suzuki A, Kobayashi M, Hoka S. Intranasal lidocaine 8% spray for second-division trigeminal neuralgia. Br J Anaesth 2006;97:559-63


29. Schnell S, Marrodan M, Acosta JN, Bonamico L, Goicochea MT. Trigeminal neuralgia crisis - intravenous phenytoin as acute rescue treatment. Headache 2020;60:2247-53



31. Bergenheim AT, Asplund P, Linderoth B. Percutaneous retrogasserian balloon compression for trigeminal neuralgia: review of critical technical details and outcomes. World Neurosurg 2013;79:359-68


32. Pollock BE. Percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy for patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: a prospective analysis of factors related to pain relief. J Neurosurg 2005;102:223-8


33. Holste K, Chan AY, Rolston JD, Englot DJ. Pain outcomes following microvascular decompression for drug-resistant trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 2020;86:182-90



34. Truini A, Prosperini L, Calistri V, Fiorelli M, Pozzilli C, Millefiorini E, et al. A dual concurrent mechanism explains trigeminal neuralgia in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2016;86:2094-9


36. Rashid A, Pintea B, Kinfe TM, Surber G, Hamm K, Boström JP. LINAC stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: retrospective two-institutional examination of treatment outcomes. Radiat Oncol 2018;13:153




37. Franzini A, Messina G, Cordella R, Marras C, Broggi G. Deep brain stimulation of the posteromedial hypothalamus: indications, long-term results, and neurophysiological considerations. Neurosurg Focus 2010;29:E13

38. Burman S, Khandelwal A, Chaturvedi A. Recent advances in trigeminal neuralgia and its management: a narrative review. J Neuroanaesth Crit Care 2021;8:112-7

39. Dux M, Rosta J, Messlinger K. TRP channels in the focus of trigeminal nociceptor sensitization contributing to primary headaches. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:342



40. Ding W, You Z, Shen S, Yang J, Lim G, Doheny JT, et al. An improved rodent model of trigeminal neuropathic pain by unilateral chronic constriction injury of distal infraorbital nerve. J Pain 2017;18:899-907



41. Ahn DK, Lim EJ, Kim BC, Yang GY, Lee MK, Ju JS, et al. Compression of the trigeminal ganglion produces prolonged nociceptive behavior in rats. Eur J Pain 2009;13:568-75


42. Yeomans DC, Klukinov M. A rodent model of trigeminal neuralgia. In: Luo Z (ed). Pain Research. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 851. New York : Humana Press, 2012, pp121-31
43. Luo DS, Zhang T, Zuo CX, Zuo ZF, Li H, Wu SX, et al. An animal model for trigeminal neuralgia by compression of the trigeminal nerve root. Pain Physician 2012;15:187-96


44. An JX, He Y, Qian XY, Wu JP, Xie YK, Guo QL, et al. A new animal model of trigeminal neuralgia produced by administration of cobra venom to the infraorbital nerve in the rat. Anesth Analg 2011;113:652-6


45. Tzabazis AZ, Klukinov M, Feliciano DP, Wilson SP, Yeomans DC. Gene therapy for trigeminal pain in mice. Gene Ther 2014;21:422-6




46. Montera MA, Westlund KN. Minimally invasive oral surgery induction of the FRICT-ION chronic neuropathic pain model. Bio Protoc 2020;10:e3591



47. Zhao LX, Jiang M, Bai XQ, Cao DL, Wu XB, Zhang J, et al. TLR8 in the Trigeminal ganglion contributes to the maintenance of trigeminal neuropathic pain in mice. Neurosci Bull 2021;37:550-62




48. Li Q, Ma TL, Qiu YQ, Cui WQ, Chen T, Zhang WW, et al. Connexin 36 mediates orofacial pain hypersensitivity through GluK2 and TRPA1. Neurosci Bull 2020;36:1484-99




49. Dong W, Jin SC, Allocco A, Zeng X, Sheth AH, Panchagnula S, et al. Exome sequencing implicates impaired GABA signaling and neuronal ion transport in trigeminal neuralgia. iScience 2020;23:101552



50. Li L, Yao L, Wang F, Zhang Z. Knock-down of JAK2 and PTEN on pain behavior in rat model of trigeminal neuropathic pain. Gene 2019;719:144080


51. Guo Z, Qiu CS, Jiang X, Zhang J, Li F, Liu Q, et al. TRESK K+ channel activity regulates trigeminal nociception and headache. eNeuro 2019;6:ENEURO.0236-19.2019



52. Rozas P, Lazcano P, Piña R, Cho A, Terse A, Pertusa M, et al. Targeted overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-α increases cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity and TRPV1-dependent Ca2+ influx in trigeminal neurons. Pain 2016;157:1346-62



53. Wang SY, Wang YL, Liu FZ, Wang XZ, Zhang L, Li YF. [Experimental study of a new animal model with trigeminal neuralgia produced by administration of talc to peripheral infraobital nerve in rats]. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue 2018;27:472-6. Chinese

54. Xiong W, Wu RP, Tan MX, Tong ZJ, He LK, Guan S, et al. Emodin inhibits the expression of receptor and calcitonin-gene-related peptide release in trigeminal ganglia of trigeminal neuralgia rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10:11317-25


55. Zhang L, Ma Z, Wu Z, Jin M, An L, Xue F. Curcumin improves chronic pain induced depression through regulating serum metabolomics in a rat model of trigeminal neuralgia. J Pain Res 2020;13:3479-92




56. Zhang L, Wang J, Niu C, Zhang Y, Zhu T, Huang D, et al. Activation of parabrachial nucleus - ventral tegmental area pathway underlies the comorbid depression in chronic neuropathic pain in mice. Cell Rep 2021;37:109936



57. Wang L, Long M, Wang M, Peng S, Chen G, Zhou J, et al. Trigeminal neuralgia causes neurodegeneration in rats associated with upregulation of the CD95/CD95L pathway. Mol Pain 2020;16:1744806920908092




58. Wu C, Xie N, Lian Y, Xu H, Chen C, Zheng Y, et al. Central antinociceptive activity of peripherally applied botulinum toxin type A in lab rat model of trigeminal neuralgia. Springerplus 2016;5:431




59. Liao CC, Lin CL, Liao KR, Li JM. Long-term beneficial effects of acupuncture with reduced risk of depression development following trigeminal neuralgia: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2020;16:2961-73



60. Zhao J, Zhang Y, Liu X, Rao Y, Fu J, Hua L, et al. Activation of SK3 channel plays a pivotal role in modulation of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurol Res 2021;43:1005-12


61. Bai X, Zhang X, Wang C, Liu Y, Liu X, Fan Y, et al. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth attenuate trigeminal neuralgia in rats. Stem Cells Int 2021;2021:8819884




62. Noorani A, Hung PS, Zhang JY, Sohng K, Laperriere N, Moayedi M, et al. Pain relief reverses hippocampal abnormalities in trigeminal neuralgia. J Pain 2022;23:141-55


-
METRICS

-
- 2 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 7,542 View
- 141 Download
- ORCID iDs
-
Young Seok Park

https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7685-6292 - Related articles
-
Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia2007 September;3(2)
Microvascular Decompression for Trigeminal Neuralgia2007 September;3(2)
Treatment Outcome of Idiopathic Trigeminal Neuralgia2006 June;2(1)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print